UNBOUND MEDIA is based on air and implementations including microwave,
laser, infrared and radio
Microwaves travels at high frequency than radio waves and provide through put as a wireless network media. Micro wave transmission requires the sender to be inside of the receiver.
Microwaves travels at high frequency than radio waves and provide through put as a wireless network media. Micro wave transmission requires the sender to be inside of the receiver.
Microwave is divide b 2 ::
- Terrestial Micro Waves
- Satellitte Micro Waves
1. Terrestrial Micro
waves:
Terrestrial Micro waves are used are used to transmit wireless signals across a few miles. Terrestrial system requires that direct parabolic antennas can be pointed to each other. These systems operate in a low Giga Hertz range. two types of antennas are used for terrestrial microwave communication are parabolic dish and horn antenna.
Terrestrial Micro waves are used are used to transmit wireless signals across a few miles. Terrestrial system requires that direct parabolic antennas can be pointed to each other. These systems operate in a low Giga Hertz range. two types of antennas are used for terrestrial microwave communication are parabolic dish and horn antenna.
A
parabolic dish antenna is good at catching a wide range of signal waves and
directing them to a common point. Every wave that is parallel to the line of
sight reflects back to the focus on a common point.
a horn antenna looks like a gigantic scoop that broadcasts the assembled signals that are deflected outward in a series of narrow parallel beams by the curve head. signals are received in a manner similar to the parabolic dish antenna and are deflected down into the stem.
a horn antenna looks like a gigantic scoop that broadcasts the assembled signals that are deflected outward in a series of narrow parallel beams by the curve head. signals are received in a manner similar to the parabolic dish antenna and are deflected down into the stem.
DISH ANTENNA
HORN ANTENNA
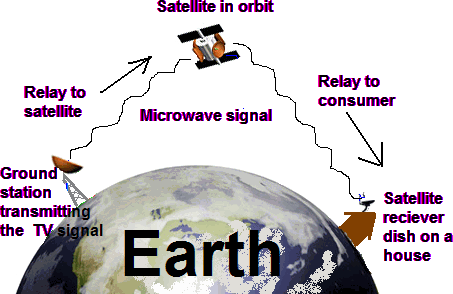
2. Satellite Micro
waves
The main problem with aero wave communication is the curvature of the earth, mountains & other structure often block the line of side. Due to this reason, many repeats are required for long distance which increases the cost of data transmission between the two points. This problem is recommended by using satellites.
Satellite micro wave transmission is used to transmit signals through out the world. These system use satellites in orbit about 50,000 Km above the earth. Satellite dishes are used to send the signals to the satellite where it is again send back down to the receiver satellite. These transmissions also use directional parabolic antenna’ with in line of side.
In satellite communication micro wave signals at 6 GHz is transmitted from a transmitter on the earth through the satellite position in space. By the time signal reaches the satellites becomes weaker due to 50,000 Km distance. The satellite amplifies week signals and transmits it back to the earth at the frequency less than 6 GHz.
The main problem with aero wave communication is the curvature of the earth, mountains & other structure often block the line of side. Due to this reason, many repeats are required for long distance which increases the cost of data transmission between the two points. This problem is recommended by using satellites.
Satellite micro wave transmission is used to transmit signals through out the world. These system use satellites in orbit about 50,000 Km above the earth. Satellite dishes are used to send the signals to the satellite where it is again send back down to the receiver satellite. These transmissions also use directional parabolic antenna’ with in line of side.
In satellite communication micro wave signals at 6 GHz is transmitted from a transmitter on the earth through the satellite position in space. By the time signal reaches the satellites becomes weaker due to 50,000 Km distance. The satellite amplifies week signals and transmits it back to the earth at the frequency less than 6 GHz.
IEEE (Institute of
Electrical and Electronics Engineers).
The IEEE describes itself as "the world's largest technical professional society; promoting the development and application of electro technology and allied sciences for the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the well-being of our members." One of the technologies they have developed is known as Ethernet 802 standard which governs local area networks (wired LANs). Ethernet governs the way in which Data Communications are done across the spectrum.
The IEEE describes itself as "the world's largest technical professional society; promoting the development and application of electro technology and allied sciences for the benefit of humanity, the advancement of the profession, and the well-being of our members." One of the technologies they have developed is known as Ethernet 802 standard which governs local area networks (wired LANs). Ethernet governs the way in which Data Communications are done across the spectrum.
Difference Between 3G
And 4G
4G - 4G speeds
are meant to exceed that of 3G. Current 3G speeds are topped out at 14Mbps
downlink and 5.8Mbps uplink. To be able to qualify as a 4G technology, speeds
of up to 100Mbps must be reached for a moving user and 1Gbps for a stationary
user. So far, these speeds are only reachable with wired LANs.
different:
1. 3G stands for 3rd generation while 4G stands for 4th generation.
2. 3G technologies are in widespread use while 4G compliant technologies are still in the horizon.
3. 4G speeds are much faster compared to 3G.
4. 3G is a mix of circuit and packet switching network while 4G is only a packet switching network.
1. 3G stands for 3rd generation while 4G stands for 4th generation.
2. 3G technologies are in widespread use while 4G compliant technologies are still in the horizon.
3. 4G speeds are much faster compared to 3G.
4. 3G is a mix of circuit and packet switching network while 4G is only a packet switching network.
Cellular phone
is a device that can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile phone operator, allowing access to the public telephone network. By contrast, a cordless telephone is used only within the short range of a single, private base station.
In addition to telephony, modern mobile phones also support a wide variety of other services such as text messaging, MMS, email, Internet access, short-range wireless communications (infrared, Bluetooth), business applications, gaming and photography. Mobile phones that offer these and more general computing capabilities are referred to as smartphones.
is a device that can make and receive telephone calls over a radio link whilst moving around a wide geographic area. It does so by connecting to a cellular network provided by a mobile phone operator, allowing access to the public telephone network. By contrast, a cordless telephone is used only within the short range of a single, private base station.
In addition to telephony, modern mobile phones also support a wide variety of other services such as text messaging, MMS, email, Internet access, short-range wireless communications (infrared, Bluetooth), business applications, gaming and photography. Mobile phones that offer these and more general computing capabilities are referred to as smartphones.
Radio frequency (RF)
is a rate of oscillation in the range of about
3 kHz to 300 GHz, which corresponds to
the frequency of radio waves, and the alternating
currents which carry radio signals. RF usually refers to electrical rather
than mechanical oscillations, although mechanical RF systems do exist.
Uplink and downlink
In satellite telecommunication, a downlink is the link from a satellite down to one or more ground stations or receivers, and an uplink is the link from a ground station up to a satellite. Some companies sell uplink and downlink services to television stations, corporations, and to other telecommunication carriers. A company can specialize in providing uplinks, downlinks, or both.
The following table shows the main frequency bands used for satellite links.
In satellite telecommunication, a downlink is the link from a satellite down to one or more ground stations or receivers, and an uplink is the link from a ground station up to a satellite. Some companies sell uplink and downlink services to television stations, corporations, and to other telecommunication carriers. A company can specialize in providing uplinks, downlinks, or both.
The following table shows the main frequency bands used for satellite links.
| Frequency Band | Downlink | Uplink |
|---|---|---|
| C | 3,700-4,200 Mhz | 5,925-6,425 MHz |
| Ku | 11.7-12.2 GHz | 14.0-14.5 GHz |
| Ka | 17.7-21.2 GHz | 27.5-31.0 GHz |
-
No comments:
Post a Comment